Lower left abdominal pain? Find out what’s causing it & how to treat it
Understanding the possible reasons behind your pain and when to seek medical care.
Lower left abdominal pain? Find out what’s causing it & how to treat it
Understanding the possible reasons behind your pain and when to seek medical care.

Lower left abdominal pain can range from mild discomfort to severe distress, affecting people of all ages. The cause may be linked to digestive issues, infections, or other underlying conditions. The type of pain—whether sharp, cramping, dull, or persistent—can provide clues about the source of the issue. Some cases may resolve on their own, while others may require medical attention to prevent complications.
Factors such as diet, lifestyle, and pre-existing health conditions may also influence the severity and frequency of the pain. In some instances, symptoms may worsen after eating certain foods, during periods of stress, or with physical activity. Understanding what triggers your pain and recognising any accompanying symptoms could help guide the right course of action for treatment and relief. Identifying the cause early may help with timely management and a better quality of life.
Lower left abdominal pain can range from mild discomfort to severe distress, affecting people of all ages. The cause may be linked to digestive issues, infections, or other underlying conditions. The type of pain—whether sharp, cramping, dull, or persistent—can provide clues about the source of the issue. Some cases may resolve on their own, while others may require medical attention to prevent complications.
Factors such as diet, lifestyle, and pre-existing health conditions may also influence the severity and frequency of the pain. In some instances, symptoms may worsen after eating certain foods, during periods of stress, or with physical activity. Understanding what triggers your pain and recognising any accompanying symptoms could help guide the right course of action for treatment and relief. Identifying the cause early may help with timely management and a better quality of life.

Common symptoms associated with lower left abdominal pain
The symptoms accompanying the pain may vary depending on the underlying condition.
Mild symptoms
- Bloating, gas, or changes in bowel habits
- Nausea, vomiting, or a reduced appetite
Severe symptoms
- Fever or chills could suggest an infection
- Pain that worsens with movement or eating

Common symptoms associated with lower left abdominal pain
The symptoms accompanying the pain may vary depending on the underlying condition.
Mild symptoms
- Bloating, gas, or changes in bowel habits
- Nausea, vomiting, or a reduced appetite
Severe symptoms
- Fever or chills could suggest an infection
- Pain that worsens with movement or eating

Possible causes of lower left abdominal pain
There are multiple potential causes of the pain, ranging from minor digestive discomfort to more complex medical conditions. These include:
- Diverticulitis: A condition where small pouches in the colon become inflamed, leading to sharp pain, often in adults over 40.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): This gastrointestinal condition is characterised by cramping, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
- Kidney stones: These are small deposits that can cause intense pain that radiates from the lower left abdomen to the back or groin.
- Gynaecological conditions: Ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or ectopic pregnancy may contribute to pain in the lower left abdominal area.
Possible causes of lower left abdominal pain
There are multiple potential causes of the pain, ranging from minor digestive discomfort to more complex medical conditions. These include:
- Diverticulitis: A condition where small pouches in the colon become inflamed, leading to sharp pain, often in adults over 40.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): This gastrointestinal condition is characterised by cramping, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
- Kidney stones: These are small deposits that can cause intense pain that radiates from the lower left abdomen to the back or groin.
- Gynaecological conditions: Ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or ectopic pregnancy may contribute to pain in the lower left abdominal area.
When to seek medical help
While some causes of the pain are mild and short-lived, certain symptoms may indicate a more serious issue that requires medical attention. These symptoms are:
- Severe or persistent pain: If the discomfort lasts more than a few hours or progressively worsens, get evaluated.
- Signs of infection: Fever, chills, or an elevated white blood cell count may suggest an infection requiring treatment.
- Difficulty passing stool or urine: This could point to a blockage in the lower intestines or kidney-related issues.
- Unexplained weight loss: If accompanied by persistent pain, weight loss may indicate a more serious medical condition.

When to seek medical help
While some causes of the pain are mild and short-lived, certain symptoms may indicate a more serious issue that requires medical attention. These symptoms are:
- Severe or persistent pain: If the discomfort lasts more than a few hours or progressively worsens, get evaluated.
- Signs of infection: Fever, chills, or an elevated white blood cell count may suggest an infection requiring treatment.
- Difficulty passing stool or urine: This could point to a blockage in the lower intestines or kidney-related issues.
- Unexplained weight loss: If accompanied by persistent pain, weight loss may indicate a more serious medical condition.
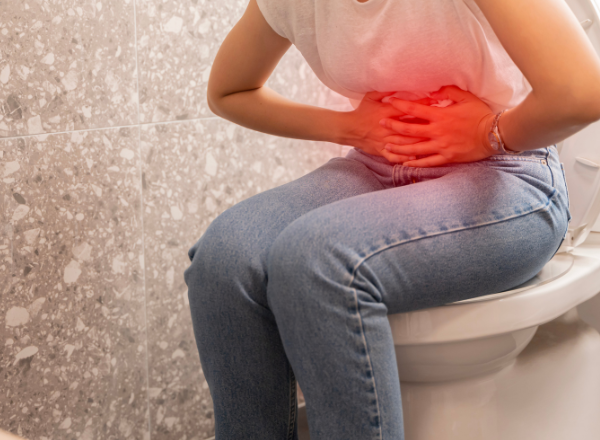

Diagnostic methods
To determine the cause of lower left abdominal pain, medical professionals may use a combination of the following diagnostic tests:
- Physical examination: A doctor may check for tenderness, swelling, or abnormal masses.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or X-rays can provide images of internal organs.
- Blood and urine tests: These help detect infections, inflammation, or kidney-related issues.
- Colonoscopy: May be recommended to evaluate concerns related to the large intestine.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the cause of lower left abdominal pain, medical professionals may use a combination of the following diagnostic tests:
- Physical examination: A doctor may check for tenderness, swelling, or abnormal masses.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or X-rays can provide images of internal organs.
- Blood and urine tests: These help detect infections, inflammation, or kidney-related issues.
- Colonoscopy: May be recommended to evaluate concerns related to the large intestine.
Treatment options
The right treatment for lower left abdominal pain depends on the underlying cause. Common approaches include:
- Medication: Pain relievers, antibiotics for infections, or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
- Dietary changes: A fibre-rich diet may help manage digestive conditions such as IBS and constipation.
- Hydration and rest: Drinking adequate fluids is essential for kidney health and overall digestive function.
- Surgical intervention: In cases such as ruptured diverticula or ovarian torsion, surgery may be required.

Treatment options
The right treatment for lower left abdominal pain depends on the underlying cause. Common approaches include:
- Medication: Pain relievers, antibiotics for infections, or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
- Dietary changes: A fibre-rich diet may help manage digestive conditions such as IBS and constipation.
- Hydration and rest: Drinking adequate fluids is essential for kidney health and overall digestive function.
- Surgical intervention: In cases such as ruptured diverticula or ovarian torsion, surgery may be required.

Don’t ignore persistent pain—get the right care
Abdominal pain, such as a burning sensation in the stomach, may sometimes be caused by minor issues, but ongoing discomfort may point to something more serious. Ignoring persistent symptoms could lead to complications that might be preventable with early medical attention.
A healthcare professional can assess your symptoms, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend the best treatment plan for your situation. Whether it’s a digestive issue or another underlying condition, timely care may make a significant difference in your overall health and well-being. If your pain isn’t going away, now is the time to seek advice—taking action today could help you feel better and avoid unnecessary complications down the road.

Don’t ignore persistent pain—get the right care
Abdominal pain, such as a burning sensation in the stomach, may sometimes be caused by minor issues, but ongoing discomfort may point to something more serious. Ignoring persistent symptoms could lead to complications that might be preventable with early medical attention.
A healthcare professional can assess your symptoms, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend the best treatment plan for your situation. Whether it’s a digestive issue or another underlying condition, timely care may make a significant difference in your overall health and well-being. If your pain isn’t going away, now is the time to seek advice—taking action today could help you feel better and avoid unnecessary complications down the road.

FAQs
Can stress contribute to pain in the lower left abdomen?
Yes, stress may impact digestion and may trigger or worsen conditions such as IBS, leading to cramping and discomfort in the lower left abdomen.
What foods should I avoid if I have frequent pain in the lower left abdomen?
Certain foods, including highly processed items, spicy meals, and dairy (for those with lactose intolerance), may aggravate digestive conditions that cause pain.
Can dehydration cause pain in the lower left abdomen?
Dehydration may contribute to kidney stone formation, which may lead to sharp pain in the lower left abdominal area.
Are there any at-home remedies for mild pain in the lower left abdomen?
Applying a warm compress, staying hydrated, and eating light, easy-to-digest foods may help alleviate mild discomfort. However, if symptoms persist, a medical consultation is recommended.
