Watery bowel movements in children: Causes, concerns, and treatment
Learn about the possible causes of diarrhoea in children, when to seek medical help, and the best treatment options to ensure your child’s well-being.
Watery bowel movements in children: Causes, concerns, and treatment
Learn about the possible causes of diarrhoea in children, when to seek medical help, and the best treatment options to ensure your child’s well-being.
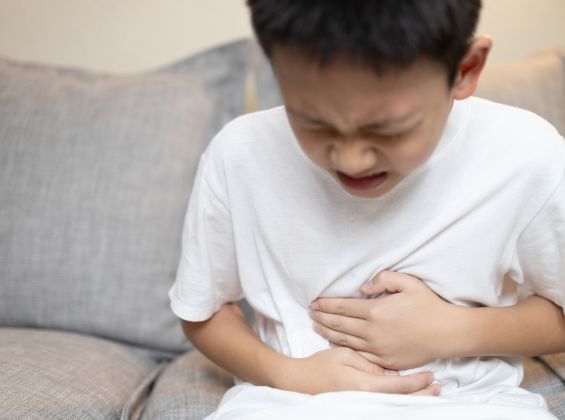

Watery bowel movements, commonly known as diarrhoea and loose bowel movements, occur when a child passes loose or watery stools more frequently than usual. While occasional diarrhoea is common and often resolves on its own, persistent or severe cases may indicate an underlying issue that requires attention. Understanding the causes and symptoms can help parents take the right steps to manage their child’s health effectively.
Watery bowel movements, commonly known as diarrhoea and loose bowel movements, occur when a child passes loose or watery stools more frequently than usual. While occasional diarrhoea is common and often resolves on its own, persistent or severe cases may indicate an underlying issue that requires attention. Understanding the causes and symptoms can help parents take the right steps to manage their child’s health effectively.

Understanding watery bowel movements in children
What causes watery stools in children?
Watery stools in children can be caused by viral infections like rotavirus and norovirus, bacterial infections such as Salmonella and E. coli, food intolerances, or medications like antibiotics that disrupt gut bacteria.
Age-related factors
Age influences the causes of watery stools. Infants may have diarrhoea due to formula intolerance, while toddlers are more prone to infections. Older children may experience digestive issues from stress or conditions like IBS.
Symptoms associated with diarrhoea
In addition to watery stools, symptoms like a high fever, fatigue, chills, loss of appetite and abdominal pain may occur. If your child experiences dehydration, weight loss, or blood in the stool, seek medical advice promptly.
When it’s normal vs. abnormal
Occasional watery stools due to diet changes are usually harmless. However, if diarrhoea lasts over 48 hours or is accompanied by vomiting, fever, or blood in the stool, medical attention is needed to prevent dehydration.

Understanding watery bowel movements in children
What causes watery stools in children?
Watery stools in children can be caused by viral infections like rotavirus and norovirus, bacterial infections such as Salmonella and E. coli, food intolerances, or medications like antibiotics that disrupt gut bacteria.
Age-related factors
Age influences the causes of watery stools. Infants may have diarrhoea due to formula intolerance, while toddlers are more prone to infections. Older children may experience digestive issues from stress or conditions like IBS.
Symptoms associated with diarrhoea
In addition to watery stools, symptoms like a high fever, fatigue, chills, loss of appetite and abdominal pain may occur. If your child experiences dehydration, weight loss, or blood in the stool, seek medical advice promptly.
When it’s normal vs. abnormal
Occasional watery stools due to diet changes are usually harmless. However, if diarrhoea lasts over 48 hours or is accompanied by vomiting, fever, or blood in the stool, medical attention is needed to prevent dehydration.

Common causes of loose bowel movements in children
Viral Infections
Rotavirus and norovirus are the leading causes of diarrhoea in small children. These viral infections can often cause significant discomfort but usually resolve within a few days. Also, hydration is key to managing symptoms.
Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections can cause more severe diarrhoea and may require medical intervention. Symptoms often include high fever and bloody stools. Practising good hygiene and food safety can reduce the risk of bacterial infections.
Food intolerances or allergies
Lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity can lead to chronic diarrhoea and digestive discomfort. Identifying trigger foods and eliminating them from your child’s diet is an effective way to manage diarrhoea-related symptoms.
Medications and antibiotics
Certain medications, particularly antibiotics, can upset the balance of gut bacteria and cause temporary diarrhoea. Probiotics can help restore gut health, but it’s important to consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
Common causes of loose bowel movements in children
Viral Infections
Rotavirus and norovirus are the leading causes of diarrhoea in small children. These viral infections can often cause significant discomfort but usually resolve within a few days. Also, hydration is key to managing symptoms.
Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections can cause more severe diarrhoea and may require medical intervention. Symptoms often include high fever and bloody stools. Practising good hygiene and food safety can reduce the risk of bacterial infections.
Food intolerances or allergies
Lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity can lead to chronic diarrhoea and digestive discomfort. Identifying trigger foods and eliminating them from your child’s diet is an effective way to manage diarrhoea-related symptoms.
Medications and antibiotics
Certain medications, particularly antibiotics, can upset the balance of gut bacteria and cause temporary diarrhoea. Probiotics can help restore gut health, but it’s important to consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
When to be concerned about loose bowel movements
Severe dehydration
If your child shows signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth or lethargy, it’s important to seek medical help. Rehydration solutions are critical in restoring lost fluids and electrolytes.
Blood in the stool
Blood in the stool is a red flag and may indicate a more serious underlying issue, such as a bacterial infection or gastrointestinal disorder. Immediate medical attention is necessary.
Diarrhoea lasting more than 48 hours
If diarrhoea lasts for more than two days, it’s important to consult a gastrointestinal specialist to rule out underlying conditions and prevent further complications like dehydration.
Accompanying fever or vomiting
If diarrhoea is accompanied by a high fever or vomiting, medical consultation is highly recommended. These symptoms could indicate a more severe infection or underlying condition.

When to be concerned about loose bowel movements
Severe dehydration
If your child shows signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth or lethargy, it’s important to seek medical help. Rehydration solutions are critical in restoring lost fluids and electrolytes.
Blood in the stool
Blood in the stool is a red flag and may indicate a more serious underlying issue, such as a bacterial infection or gastrointestinal disorder. Immediate medical attention is necessary.
Diarrhoea lasting more than 48 hours
If diarrhoea lasts for more than two days, it’s important to consult a gastrointestinal specialist to rule out underlying conditions and prevent further complications like dehydration.
Accompanying fever or vomiting
If diarrhoea is accompanied by a high fever or vomiting, medical consultation is highly recommended. These symptoms could indicate a more severe infection or underlying condition.


When to seek medical attention
Signs of severe dehydration
If your child is showing signs of severe dehydration, such as extreme thirst, dizziness, or fainting, you should seek immediate medical help.
Bloody stools or mucus
If you notice blood or mucus in your child’s stool, it may mean a serious underlying condition. Immediate medical consultation is essential.
Inability to keep fluids down
If your child is vomiting and unable to keep fluids down, medical intervention is necessary to prevent dehydration and provide proper treatment.
Persistent symptoms despite treatment
If your child’s symptoms don’t improve with home care and rehydration, it’s time to seek professional help to ensure appropriate treatment.
When to seek medical attention
Signs of severe dehydration
If your child is showing signs of severe dehydration, such as extreme thirst, dizziness, or fainting, you should seek immediate medical help.
Bloody stools or mucus
If you notice blood or mucus in your child’s stool, it may mean a serious underlying condition. Immediate medical consultation is essential.
Inability to keep fluids down
If your child is vomiting and unable to keep fluids down, medical intervention is necessary to prevent dehydration and provide proper treatment.
Persistent symptoms despite treatment
If your child’s symptoms don’t improve with home care and rehydration, it’s time to seek professional help to ensure appropriate treatment.

Act now if your child is struggling with watery bowel movements
While occasional watery stools can be a normal part of childhood, ongoing or severe diarrhoea should not be ignored. It could point to a more serious issue, such as a viral or bacterial infection, food intolerance, or an underlying digestive disorder that requires prompt attention. Delaying action can lead to dehydration and further complications, especially in younger children.
If your child has been experiencing frequent diarrhoea, noticeable changes in stool consistency, or symptoms like fever, dehydration, yellow mucus in the stool or blood in the stool, it’s essential to seek medical advice without delay. Early intervention can help prevent more serious health concerns and ensure your child receives the right treatment to feel better sooner. Don’t wait for it to resolve on its own—taking action now can make all the difference.

Act now if your child is struggling with watery bowel movements
While occasional watery stools can be a normal part of childhood, ongoing or severe diarrhoea should not be ignored. It could point to a more serious issue, such as a viral or bacterial infection, food intolerance, or an underlying digestive disorder that requires prompt attention. Delaying action can lead to dehydration and further complications, especially in younger children.
If your child has been experiencing frequent diarrhoea, noticeable changes in stool consistency, or symptoms like fever, dehydration, yellow mucus in the stool or blood in the stool, it’s essential to seek medical advice without delay. Early intervention can help prevent more serious health concerns and ensure your child receives the right treatment to feel better sooner. Don’t wait for it to resolve on its own—taking action now can make all the difference.

FAQs
What causes watery stools in children?
Common causes of watery stools include viral and bacterial infections, food intolerances, and medications.
Can watery bowel movements be caused by stress or anxiety?
Yes, emotional stress can sometimes lead to digestive disturbances, including temporary diarrhoea.
Is it safe to give my child medication for diarrhoea?
Some over-the-counter medications are safe for children, but it’s essential to consult a doctor before administering them, especially in young children.
How long should I wait before seeing a doctor for watery stools?
If your child’s diarrhoea lasts more than 48 hours or is accompanied by severe symptoms, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider.
